0042. Trapping Rain Water¶
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
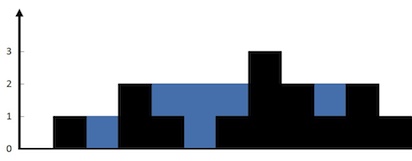
Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
Example 2:
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
Output: 9
Constraints:
n == height.length0 <= n <= 3 * 1040 <= height[i] <= 105
Analysis¶
To trap water, there should be a U shape, which means we need to have three points: left (high), mid (low), and right (high). To find satisfying points, we need to maintain a monotonic stack, which only accepts points that are less than the current one, so that when new points come in, we can find the satisfied three points.
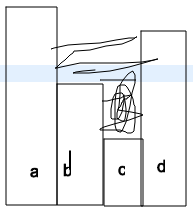
Taking this example, we can see that for d, it will start trap water for b, c, d first: area = (min(b, d) - c) * (distance between b and d). We can do this calculation for a, b, d as well: area = (min(a, d) - b) * (distance between a and d). By observation, we can see that we are just calculating the area in the rectangular: lying down with height as the height difference and width is the distance between two bars.
- Time: O(n) we push each element exactly once, and we pop each element exactly once.
- Space: O(n) the stack can contain all the elements.
Code¶
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
int n = height.size(), res = 0;
stack<int> st;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (st.empty()) st.push(i);
else {
while (!st.empty() && height[st.top()] < height[i]) {
int t = st.top();
st.pop();
if (st.empty()) break;
res += (i - st.top() - 1) * (min(height[i], height[st.top()]) - height[t]);
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
};