0138. Copy list with Random Pointer¶
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand newnodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) that therandompointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1: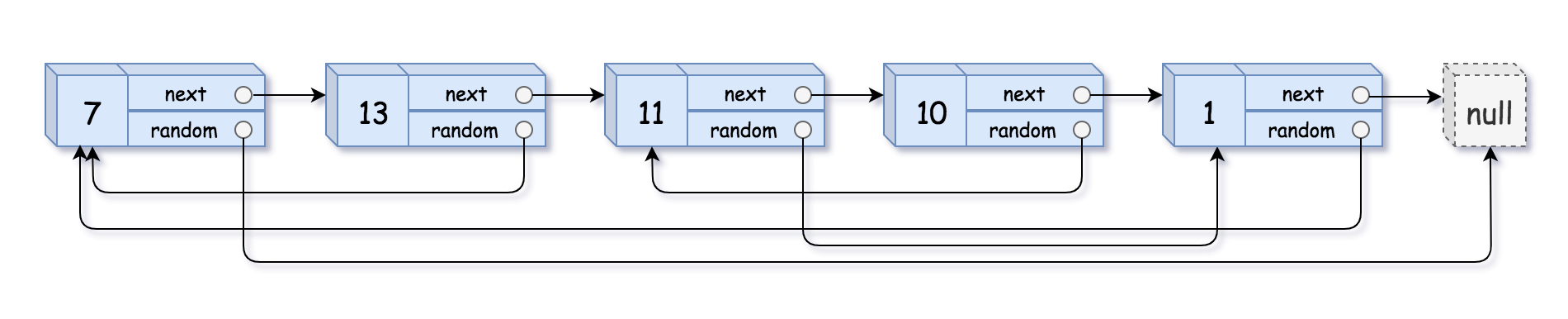
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
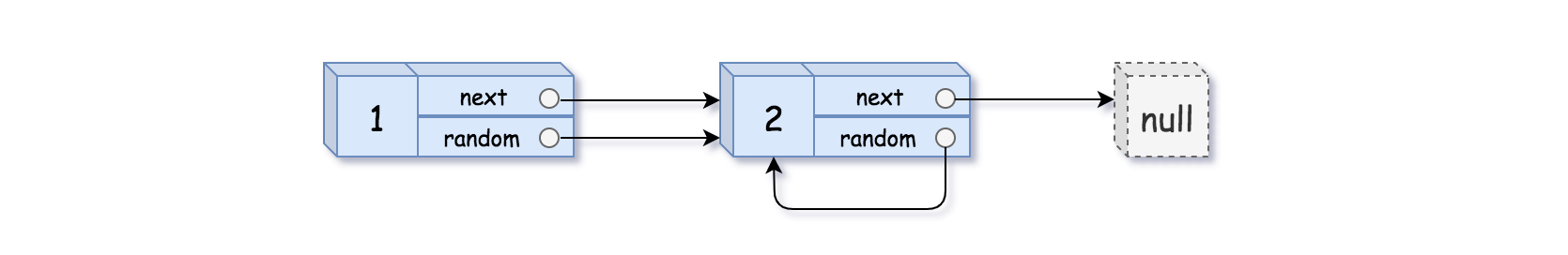
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
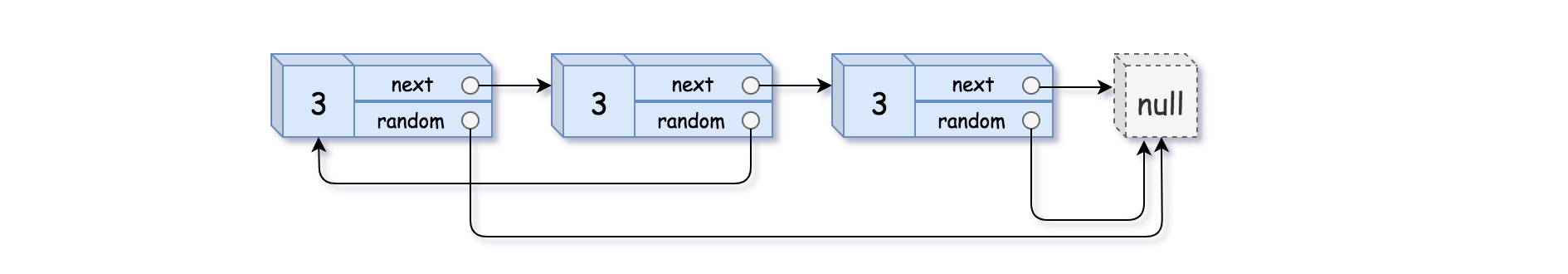
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: The given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomisnullor is pointing to some node in the linked list.
算法1¶
迭代+哈希表 O(n)¶
因为使用next节点可以保证遍历到所有的节点,所以我们使用next节点进行遍历。在遍历的时候每次把next节点放入哈希表中,这样方便检查在检查是否生成random节点中防止重复生成。
时间复杂度¶
因为每次遍历整个链表需要O(n),空间上不算生成的节点需要O(2 \times n)来建立哈希表。
C++ 代码¶
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
Node* newHead = new Node(head -> val);
Node* cpy = newHead;
m[head] = newHead; // don't forget to put newHead into the map!!!
while (head) {
if (head -> next) {
if (!m.count(head -> next))
m[head -> next] = new Node(head -> next -> val);
cpy -> next = m[head -> next];
}
if (head -> random) {
if (!m.count(head -> random))
m[head -> random] = new Node(head -> random -> val);
cpy -> random = m[head -> random];
}
head = head -> next;
cpy = cpy -> next;
}
return newHead;
}
};
算法2¶
递归+哈希表 O(n)¶
同样的思路也可以应用于图的遍历。对于Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {这个函数的物理意义是:copy一个当前head节点和他其他所有next和random节点,并且返回这个已经copy好的节点。这样base case就很清晰:如果head是空,那么返回NULL,如果head已经存在于哈希表中,那么我们直接返回deep copy好的这个节点。
时间复杂度¶
由于每次recursion call最终会被call n次(不是random的指针的数量,因为如果多次访问已经存在的节点就可以直接剪枝使用之前已经生成的节点来返回,不会再进行递归调用),所以时间是O(n)。空间上除了哈希表的大小还需要计算call stack的大小,即O(n + 2 n)
C++ 代码¶
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
if (m.count(head)) return m[head];
Node* newHead = new Node(head -> val);
m[head] = newHead;
newHead -> next = copyRandomList(head -> next);
newHead -> random = copyRandomList(head -> random);
return newHead;
}
};
算法3¶
迭代+无哈希表 O(n)¶
- 首先在每一个curr, curr -> next中添加一个新的节点即:curr, newNext, curr -> next。
- 第二步是添加所有的random指针,注意此时所有的节点已经存在,所以只需要添加所有的random指针即可。
- 最后一步是断开所有的next节点,因为此时我们已经遍历并且安装了所有的random指针。
时间复杂度¶
因为每次遍历整个链表需要O(n),空间上不再需要使用哈希表所以是O(1).
C++ 代码¶
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* struct RandomListNode {
* int label;
* RandomListNode *next, *random;
* RandomListNode(int x) : label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
RandomListNode *copyRandomList(RandomListNode *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
RandomListNode *newHead, *l1, *l2;
for (l1 = head; l1 != NULL; l1 = l1->next->next) {
l2 = new RandomListNode(l1->label);
l2->next = l1->next;
l1->next = l2;
}
for (l1 = head; l1 != NULL; l1 = l1->next->next) {
if (l1->random) l1->next->random = l1->random->next;
}
newHead = head->next;
for (l1 = head; l1 != NULL; l1 = l1->next) {
l2 = l1->next;
l1->next = l2->next;
if (l2->next) l2->next = l2->next->next;
}
return newHead;
}
};