0099. Recover Binary Search Tree¶
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Follow up: A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward. Could you devise a constant space solution?
Example 1:
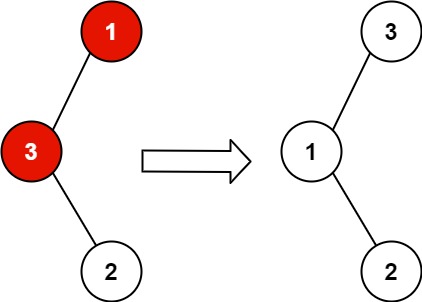
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2]
Output: [3,1,null,null,2]
Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:
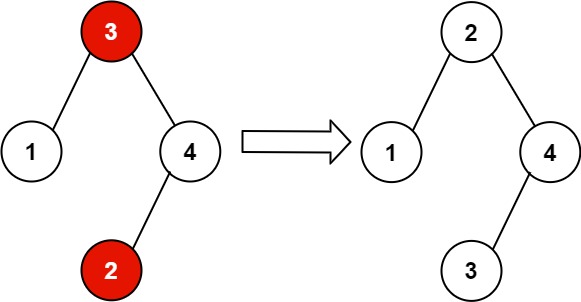
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2]
Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3]
Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Analysis¶
Use in-order tree traverse, we can find that all the left < root > right. If there is any invalid nodes, we should find left(prev) > root. We keep track of last level's root as prev where current root is it's left child.
There are two situations: 1. first isn't populated, so the first two node should be swapped are pre and root. 2. first is populated, then we traverse all the way down to find the last pre that is greater than root.
Time Complexity: O(n) as it's an in-order traversal Space Complexity: O(n) worst case the tree is a linkedlist
Code¶
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* first = NULL;
TreeNode* second = NULL;
TreeNode* prev = new TreeNode(INT_MIN);
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
help(root);
swap(first->val, second->val);
}
void help(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
help(root->left);
if (first == NULL && prev->val > root->val) first = prev;
if (first != NULL && prev->val > root->val) second = root;
prev = root;
help(root->right);
}