0114. Flatten binary tree to linked list¶
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
- The "linked list" should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The "linked list" should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
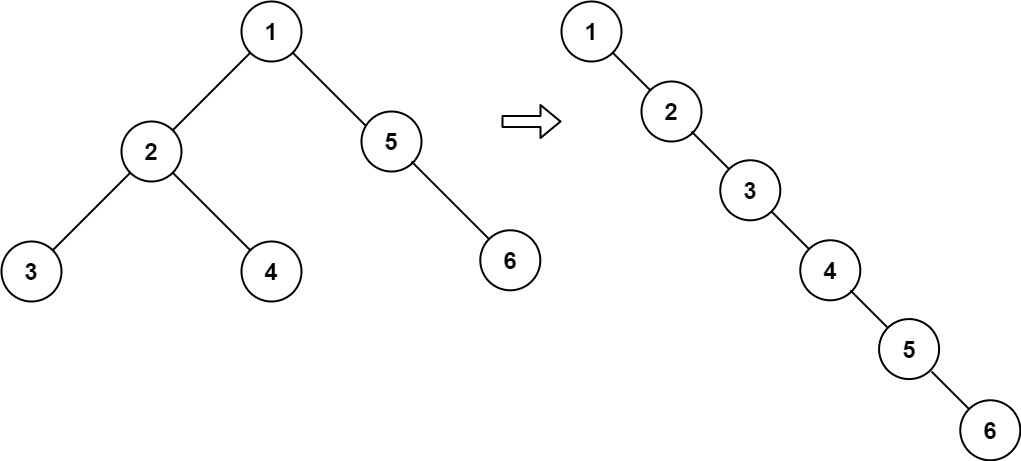
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
Analysis¶
Method 1: flatten left and right tree, then append the left to the end of right.¶
Time Complexity: if the tree is fully balanced (left height - right height abs value <= 1), then the tree will have at max log(N) levels, each node in the recursion tree, it will require log(N) runs for the while loop, so the time complexity is O(log(N) \times N)
Method 2: travese right then left, then directly append¶
我们知道题目给定的遍历顺序其实就是先序遍历的顺序,所以我们能不能利用先序遍历的代码,每遍历一个节点,就将上一个节点的右指针更新为当前节点。
先序遍历的顺序是 1 2 3 4 5 6。
遍历到 2,把 1 的右指针指向 2。1 -> 2 3 4 5 6。
遍历到 3,把 2 的右指针指向 3。1 -> 2 -> 3 4 5 6。
... ...
一直进行下去似乎就解决了这个问题。但现实是残酷的,原因就是我们把 1 的右指针指向 2,那么 1 的原本的右孩子就丢失了,也就是 5 就找不到了。
解决方法的话,我们可以逆过来进行。
我们依次遍历 6 5 4 3 2 1,然后每遍历一个节点就将当前节点的右指针更新为上一个节点。
遍历到 5,把 5 的右指针指向 6。6 <- 5 4 3 2 1。
遍历到 4,把 4 的右指针指向 5。6 <- 5 <- 4 3 2 1。
... ...
作者:windliang 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by--26/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
Code 1¶
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(root.right);
TreeNode tmp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
while (root.right != null) root = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
}
Code 2¶
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode pre = null;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
root.right = pre;
root.left = null;
pre = root;
}
}