0994. Rotting Oranges¶
You are given an m x n grid where each cell can have one of three values:
0representing an empty cell,1representing a fresh orange, or2representing a rotten orange.
Every minute, any fresh orange that is 4-directionally adjacent to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange. If this is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
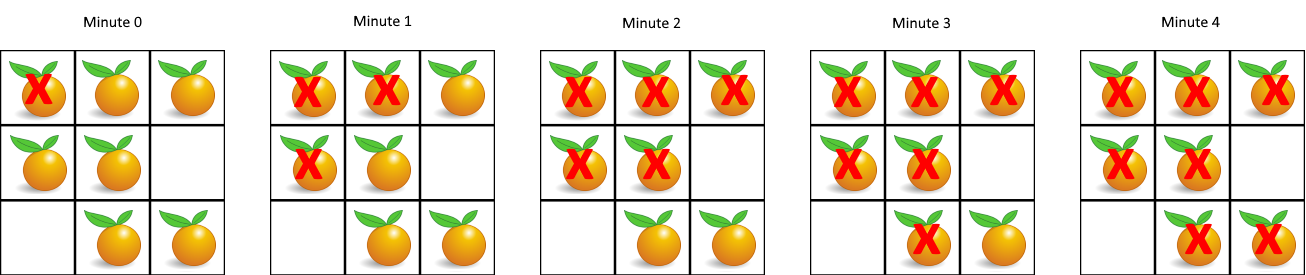
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
Output: -1
Explanation: The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[0,2]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10grid[i][j]is0,1, or2.
Analysis¶
Using bfs to expand level by level, using a counter to keep track of how many levels are there, which is the anser of our problem.
- Time Complexity: O(N) since you need to iterate through all the cells.
- Space Complexity: O(N) since the worst case is when you put all the 1s into the queue.
Code¶
class Solution {
public:
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& g) {
// step 1: check if possible
int m = g.size(), n = g[0].size();
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
vector<pair<int, int>> ones;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (g[i][j] == 2)
q.push({i,j});
else if (g[i][j] == 1)
ones.push_back({i,j});
}
// step 2: iterate all the neigbours who are currently 1
int dir[4][2] = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
int minutes = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
minutes ++;
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
int x, y;
tie(x, y) = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto d : dir) {
int dx = x + d[0], dy = y + d[1];
// error check and then set to 2 and put it to queue
if (dx < 0 || dx >= m || dy < 0 || dy >= n ||
g[dx][dy] != 1) continue;
g[dx][dy] = 2;
q.push({dx,dy});
}
}
}
// step 3: error checking
for (auto coord : ones)
if (g[coord.first][coord.second] == 1) return -1;
// if answer is 0, then return 0
return max(0, minutes - 1);
}
};
Last update:
April 1, 2022