0149. Max Points on a line¶
Given an array of points where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents a point on the X-Yplane, return the maximum number of points that lie on the same straight line.
Example 1:
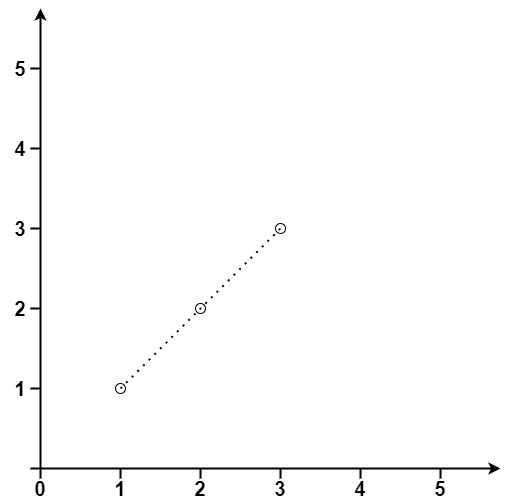
Input: points = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]]
Output: 3
Example 2:
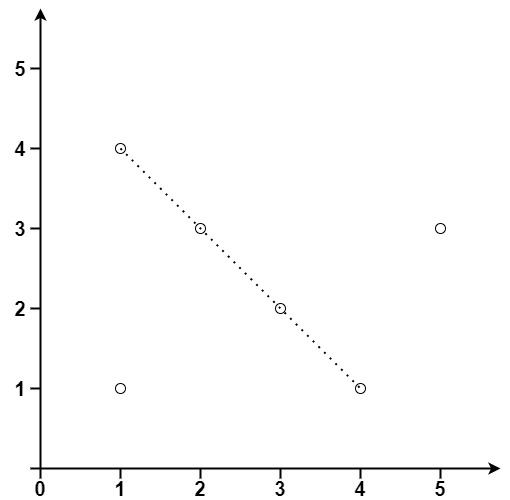
Input: points = [[1,1],[3,2],[5,3],[4,1],[2,3],[1,4]]
Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 300points[i].length == 2-104 <= xi, yi <= 104- All the
pointsare unique.
Analysis¶
In order to make sure more than two points are on the same line, any two of the points have to share the same slope. So we can use slope -> # of points with the same slope to calculate the maximum number of points on the slope. To calculate the slope, we cannot just arbitrarily choose two points, since we don't want to calculate the slope of a, b and b, a twice. To achieve this, we just need two for loop:
for i = 0 to n:
for j = i + 1 to n:
do your thing
To do so, there are two special cases to take into consideration: 1. If two points are vertical-align, then the slope would be 0 2. If two points are the same, we still need to update the result
Time Complexity: O(n^2) Space Complexity: O(n^2)
Code¶
class Solution {
public:
int maxPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
if (points.empty())
return 0;
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) {
unordered_map<long double, int> m; // slope -> num of points
int duplicate = 0, vertical = 1; // set vertical to 1 since itself also counts as one
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.size(); ++j) {
if (points[i][0] == points[j][0]) {
vertical++;
if (points[i][1] == points[j][1])
duplicate++;
}
}
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.size(); ++j) {
if (points[i][0] == points[j][0])
continue;
long double slope = (long double) (points[i][1] - points[j][1]) / (points[i][0] - points[j][0]);
if (m[slope] == 0)
m[slope] = 2;
else
m[slope]++;
res = max(res, m[slope] + duplicate);
}
res = max(res, vertical);
}
return res;
}
};